-
Home
-
About Us
-
Products
-
Video
-
News
-
Blog
-
Contact Us
Leave Your Message
Request a Quote

In the realm of animal husbandry, "Livestock Injection" is a vital technique that significantly enhances animal health. According to the Global Animal Health Industry Report 2022, improper injection can lead to over $1 billion in economic losses annually due to health complications. Proper training and technique are crucial for preventing these issues. Dr. Emily Carter, a leading expert in veterinary medicine, emphasizes, “Effective livestock injection is a fundamental pillar for sustainable animal care.”
The need for accurate injection methods, including vaccination and medication administration, cannot be overstated. Livestock Injection impacts disease prevention, growth promotion, and overall productivity. A study by the International Journal of Animal Science indicates that well-administered injections can increase livestock weight gain by up to 20%. Despite these advantages, many farmers struggle with injection techniques, risking their animals' health.
Challenges remain in achieving optimal livestock health. Inadequate training and improper techniques can lead to infections, abscesses, and poor growth rates. Farmers often overlook the importance of precision in livestock injections, leading to suboptimal outcomes. Addressing these shortcomings is vital for improving animal welfare and productivity in the livestock sector. Encouraging continued education in injection techniques could pave the way for better results in the industry.

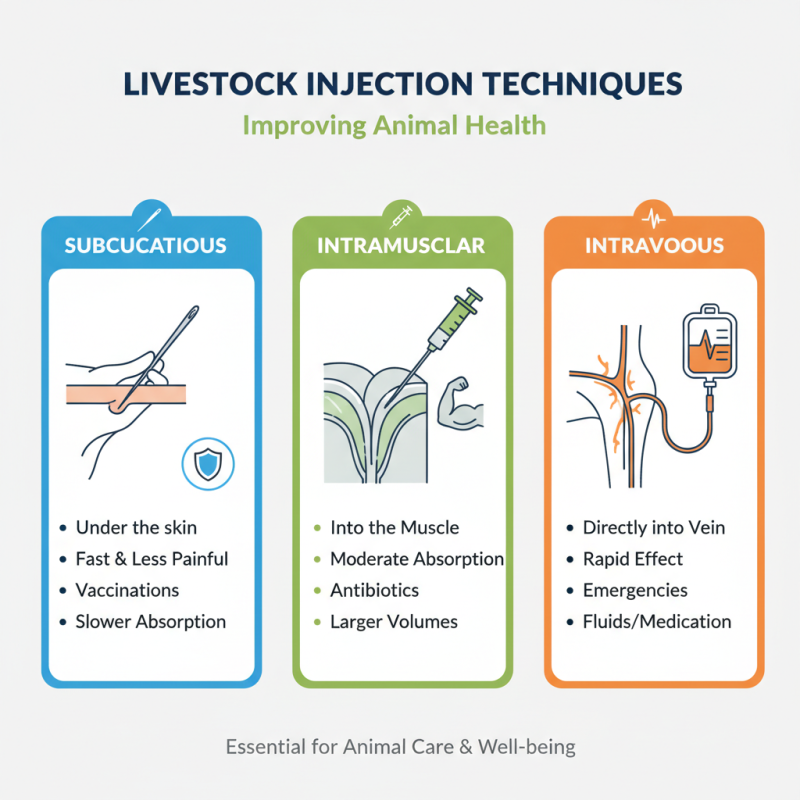
Understanding livestock injection techniques is essential for improving animal health. These methods include subcutaneous, intramuscular, and intravenous injections. Each technique has specific applications and benefits. For example, subcutaneous injections are quick and less painful, making them suitable for vaccinations. However, they may deliver slower medication absorption compared to other methods.
Intramuscular injections allow for faster medication delivery but can cause discomfort if done incorrectly. It's crucial to select the right needle size for the animal's weight and skin thickness. Many practitioners struggle with finding the right site for these injections. Improper techniques can lead to complications, such as abscesses or reduced efficacy of medications.
Regular training and practice can improve skills in livestock injections. Observing experienced colleagues can reveal nuances you might miss. Reflecting on your injection techniques can help identify areas needing improvement. Keeping records of injection sites and animal responses can provide valuable insights for future treatments.
Proper injection techniques play a crucial role in ensuring the health of livestock. When administered correctly, injections can protect animals from diseases. It can promote faster recovery when they are sick. However, improper techniques can lead to complications, including infections and abscesses. Animals may react poorly, causing distress and reducing their productivity.
Using sterile equipment is essential. The site of injection should be cleaned properly to prevent contamination. Different types of injections require different approaches. Intramuscular injections need careful placement in muscle tissue. In contrast, subcutaneous injections should be done just under the skin. Each technique has its own set of challenges, and attention to detail is vital.
Mistakes happen. Some handlers may inject too quickly or in the wrong location. This can cause pain or damage to tissues. Regular training helps improve skills. Reflecting on past experiences can lead to better practices. Learning from each injection event can build a healthier herd over time.
Administering injections to livestock is an essential skill for ensuring animal health. Start by gathering all necessary supplies. You will need the medication, syringe, and needle. Clean your hands and ensure your equipment is sterile. It's crucial to choose the right injection site. Common sites include the neck or thigh. Always check for any abnormalities in the skin before you proceed.
When you are ready, approach the animal calmly. Restraint might be necessary depending on the size and temperament. Insert the needle at the appropriate angle to avoid injury. Inject the medication slowly to help the animal adjust. Observe the animal for any immediate reactions. If you notice swelling or distress, re-evaluate your technique and the injection site.
Sometimes, the process doesn’t go perfectly. It’s not uncommon to miss the injection target. Mistakes can lead to stress for both the animal and handler. Reflect on each experience to improve your skills. Continuous practice helps you become more proficient. Each injection is a step toward better animal welfare. Remember, patience is key.
Common injection sites in livestock play a crucial role in ensuring animal health. The most widely used locations include the neck, shoulder, and thigh areas. According to the American Veterinary Medical Association, proper injection techniques can significantly reduce stress in animals. Interestingly, improper administration can lead to complications, such as abscesses or nerve damage.
For subcutaneous injections, the loose skin over the shoulder or the neck is preferred. These areas allow for easy access and rapid absorption. In contrast, intramuscular injections are typically administered in the thigh or neck muscles. Research indicates that the neck muscle is less prone to infection when perfectly executed. However, many farmers overlook this detail, risking the health of their livestock.
Intravenous injections require precision. The jugular vein is a common site, but mistakes can have serious repercussions. A study published in the Journal of Animal Science found that nearly 20% of injections in livestock were performed incorrectly. This statistic highlights a gap in training among livestock handlers. Better education on injection techniques could potentially enhance animal welfare and productivity.
Post-injection care is crucial for the health of livestock. Monitoring the injection site is essential. Research shows that 20% of injection-related complications arise from improper aftercare. Farmers should clean the area with antiseptic. This practice reduces the risk of infection. Observing the animal for signs of pain or swelling is important. If swelling occurs, apply a cold compress for relief.
Nutrition plays a vital role in recovery. Providing adequate hydration and balanced feed supports the healing process. A study indicated that 70% of livestock recover faster with proper nutrition post-injection. Ensure animals have access to fresh water at all times. Watching for behavioral changes can provide insight into recovery. An animal that is excessively lethargic may need further evaluation.
Regular health checks following injections are necessary. Monitoring vital signs can prevent serious complications. For example, elevated body temperature can indicate infection. Keeping detailed records of each injection and subsequent health indicators will aid in tracking recovery patterns. Utilizing this approach not only improves animal well-being but also enhances overall herd health.
| Animal Type | Injection Site | Injection Technique | Post-Injection Care | Monitoring Duration (Hours) | Signs of Recovery |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cattle | Neck | Intramuscular | Check for swelling and signs of infection | 48 | Increased appetite and activity |
| Sheep | Shoulder | Subcutaneous | Monitor for abnormal behavior | 24 | Resumption of normal grazing |
| Goats | Thigh | Intramuscular | Keep the animal calm and hydrated | 36 | Improved mobility and interest in feed |
| Pigs | Ear | Subcutaneous | Watch for signs of distress | 12 | Normal breathing and active behavior |